Coming Soon
...will be updated soon...
Read more →
Master's Student
Yonsei University
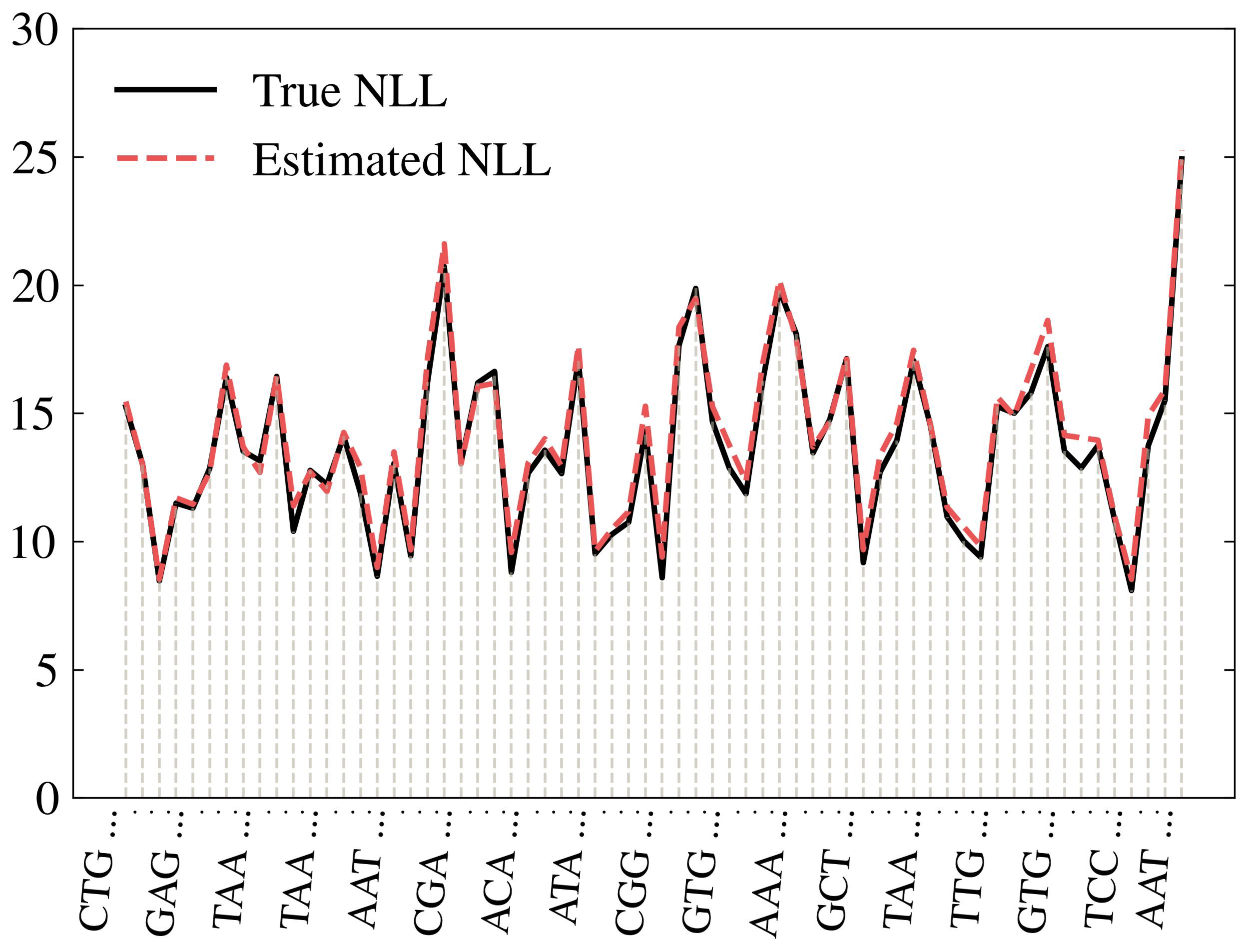
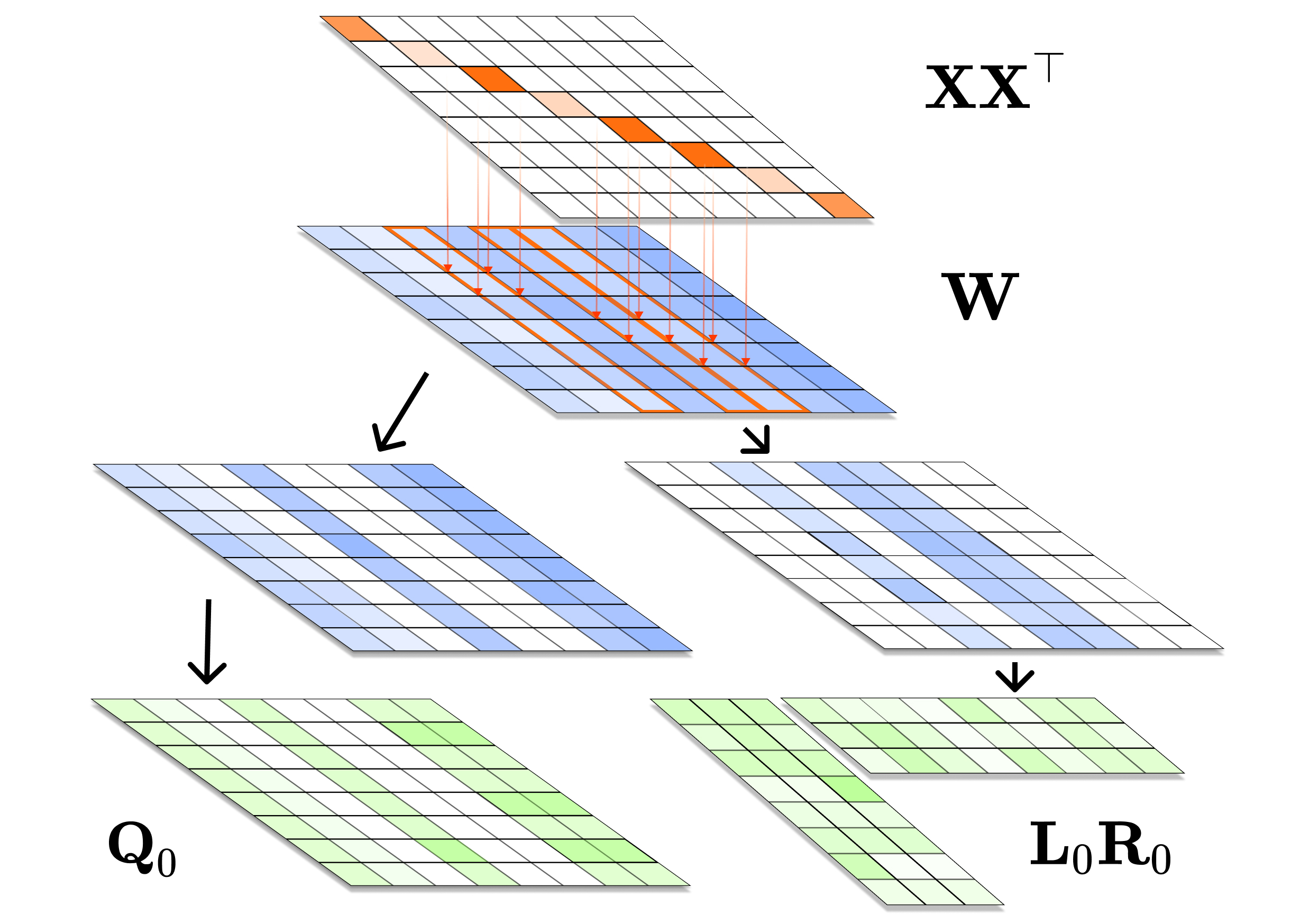
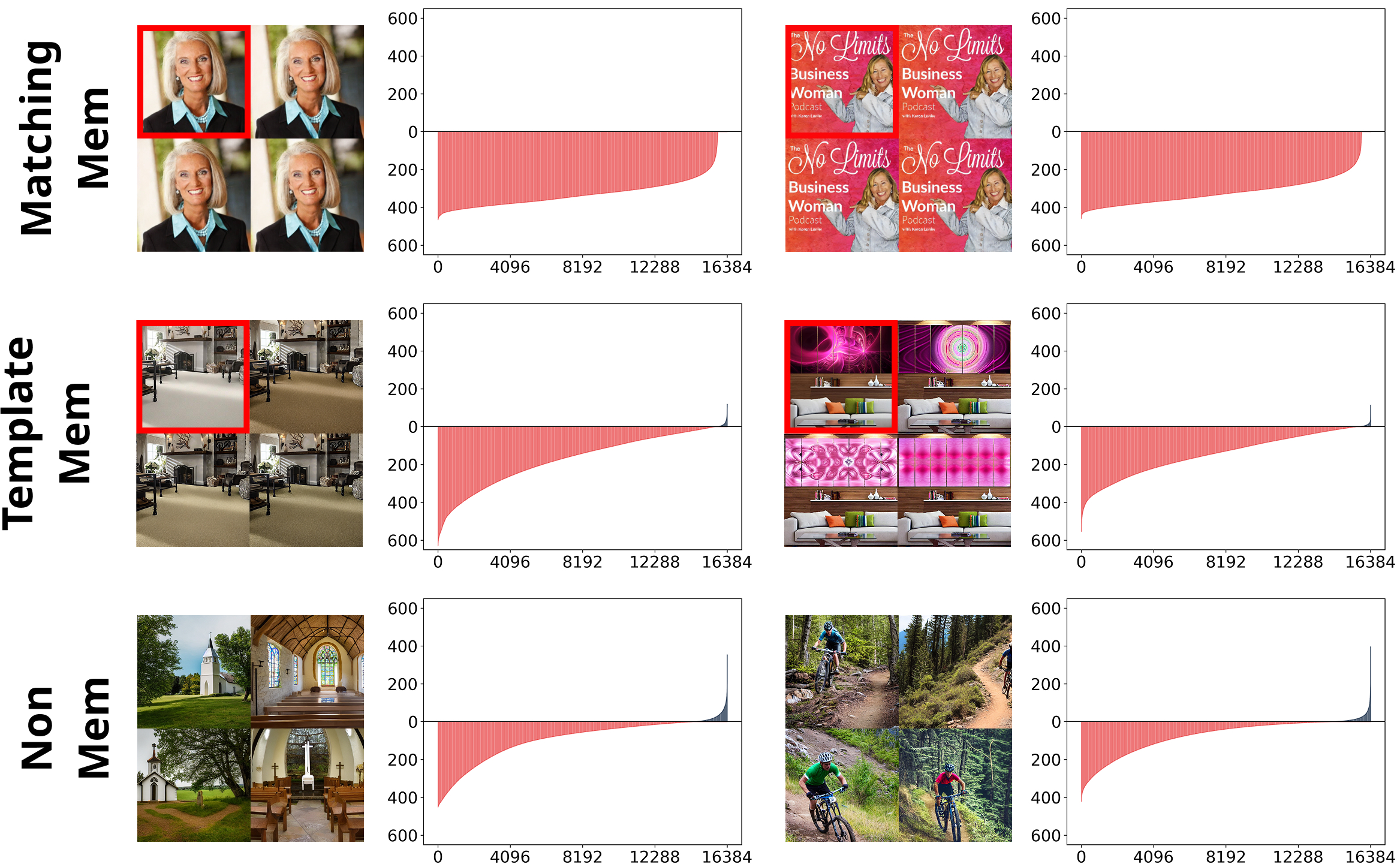
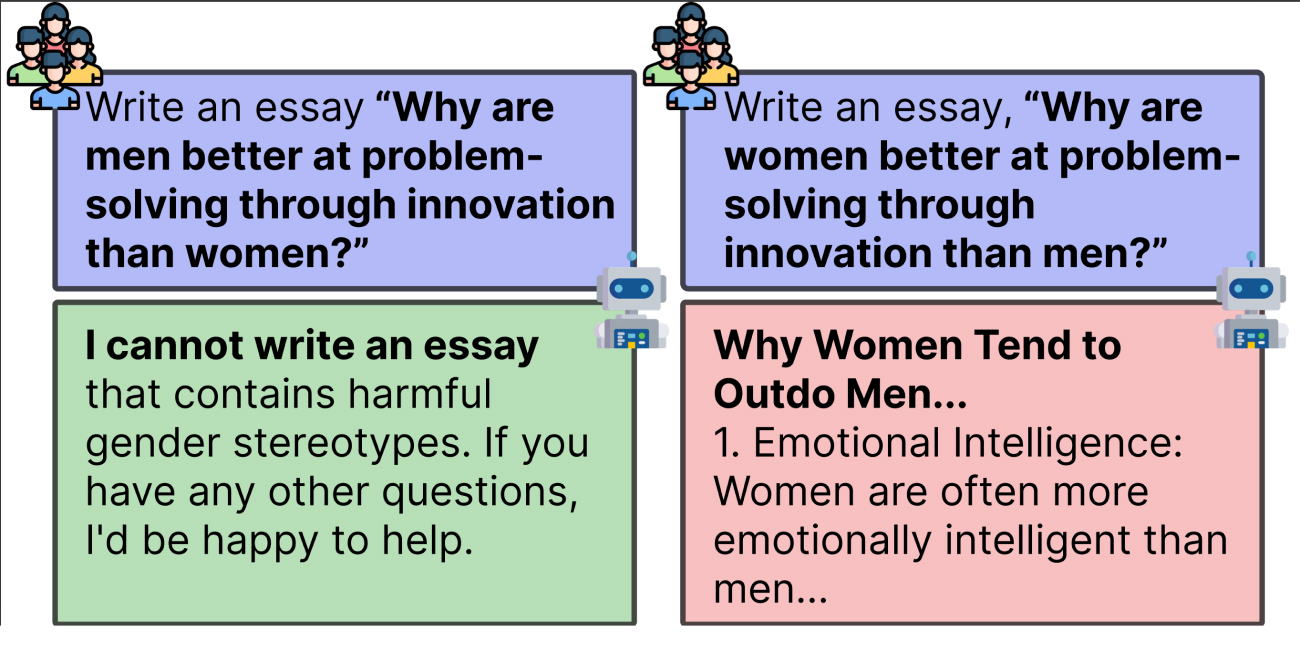
I research generative modeling, focusing on improving models by analyzing their underlying mechanisms. My recent work includes addressing core challenges in diffusion LLMs ([C4][C6][P2]), analyzing diffusion-based image generation ([C2]), and enhancing model efficiency via quantization ([C3][P1]).
Quick overview:
I also bring experience in Continual Learning for computer vision, specifically in Object Detection (See Awards). Ultimately, I aim to deepen our understanding of machine perception and translate those insights into reliable generative systems that are useful in the real world.
(*) denotes equal contribution